JavaScript Operators and Expressions
JS Operators :
- Assignment operator : Assign values to JavaScript variables
- Example: x = y
- In the next table you can see all Assignment Operators that reduce the arithmetic logic by simplifying the logic

- comparison operator : Compares its operands and returns a logical value based on whether the comparison is true.
- Example: Equal (==)
- In the following table you can see all comparison Operators

- Arithmetic operators : takes numerical values (either literals or variables) as their operands and returns a single numerical value. The standard arithmetic operators are addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), and division (/).
- All arithmetic operators listed in the following table:
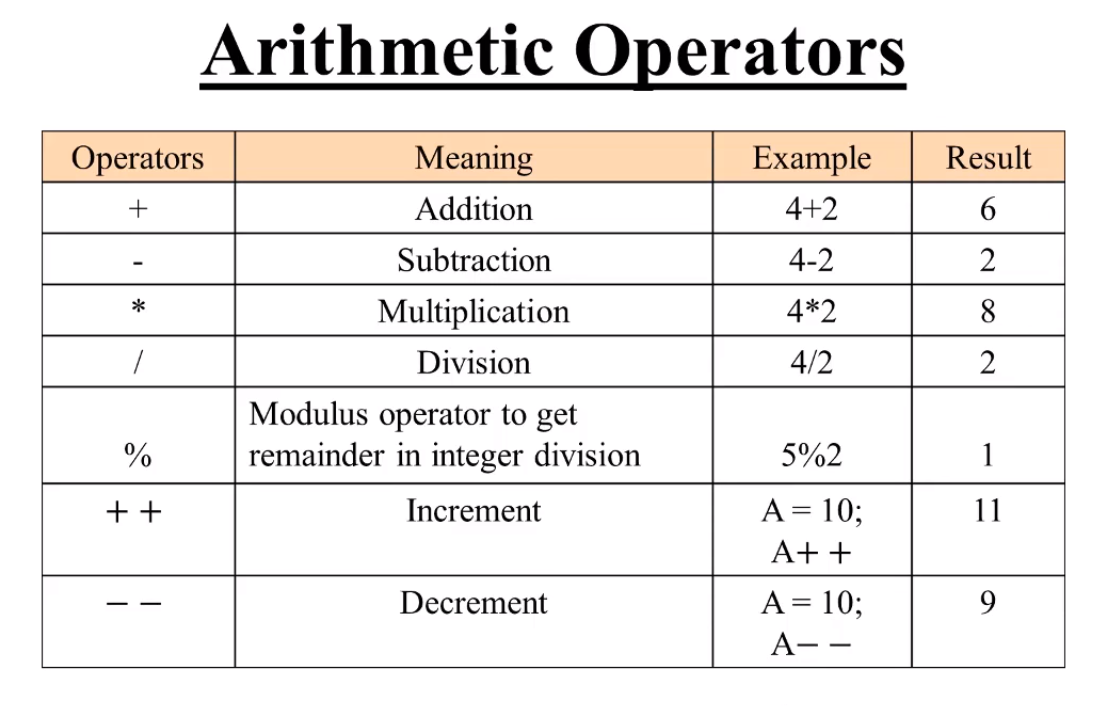
- All arithmetic operators listed in the following table:
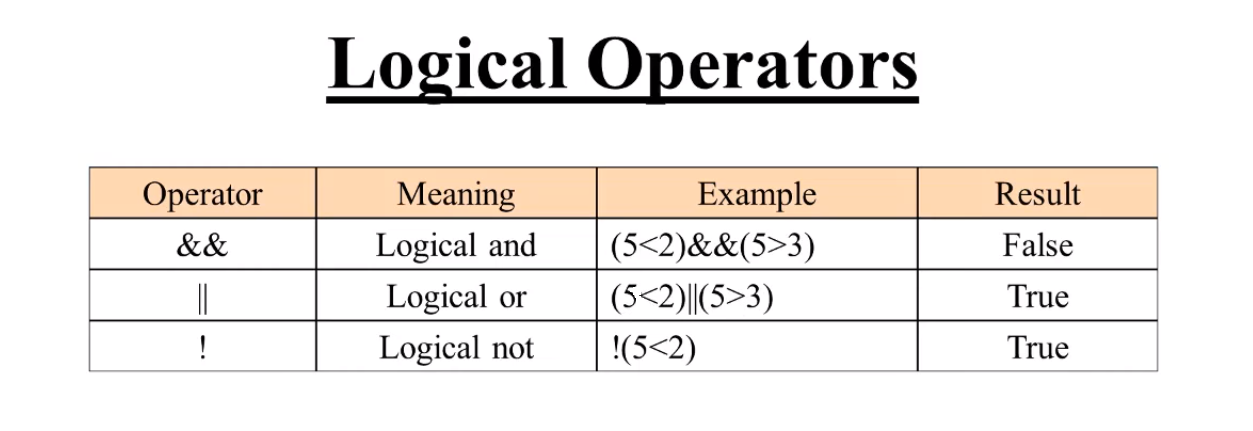
- Logical operators: uses Boolean (logical) values; Also returns a Boolean value. However, the && and || operators actually return the value of one of the specified operands, so if these operators are used with non-Boolean values, they may return a non-Boolean value. The logical operators are described in the following table.
Loops and iteration
- Execute a block of code a number of times.
There are Two different kinds of loops:
- FOR Loops : loops through a block of code a number of times
- while loops : loops through a block of code while a specified condition is true
- Example of For loop shows the syntax
for (let step = 0; step < 5; step++) {
// Runs 5 times, with values of step 0 through 4.
console.log('Walking east one step');
}
- Example of while loop that shows the syntax
let n = 0;
let x = 0;
while (n < 3) {
n++;
x += n;
}